Science Notebook
Why Are Electric Cars Occasionally Worse for the Environment than Gas Cars?




Background: Electric cars and conventional cars get their energy from relatively the same sources but are created in different places.
A conventional car uses fossil fuels to power its engine, by converting the energy stored in the fuel into kinetic energy and mechanical energy to move the car. Not all of the energy is used efficiently though, 66% of the energy in the fuel is lost by the engine as heat energy during the combustion process. The combustion of these fossil fuels is one of the main contributors to global warming because the gases released as exhaust trap heat in the atmosphere. Another 8% of the fuel’s energy is wasted while being transferred in the drivetrain or other parts of the car. This means that only about 26% of the fuel’s energy is being used to actually move the car, which is extremely inefficient (Woodford). An electrical car, on the other hand, is almost three times as efficient by using up 60% of its electrical power to move the car, only losing 40% of the energy for relatively the same reasons as the conventional car, without directly releasing greenhouse gases, earning the title of ‘environmentally friendly’ (EPA).
While the potential energy from the fuel is created into kinetic energy directly in the vehicle’s engine, an electrical car’s energy is converted to electricity at a power plant. Less than 33% of the potential energy from the combustible fuel used at a power plant is transferred into electricity because energy is lost in the process of conversion (EIA). Around another 2% is lost while the electricity travels through power lines. In the end, only about 36% of the initial energy produced reaches an electric cars’ plug, and since another 60% is lost in its engine, only 21.6% of the initial energy stored in the fuel powering the power plant is actually transferred to electric cars (NAS). This 21.6% energy efficiency can be juxtaposed to the 26% percent of initial energy used by gas cars. This means that when a power plant is run on clean fuels the electric car runs 100% cleaner than a gas car in terms of air pollution, but when the electricity powering the car comes from fossil fuels their environmental impact (in terms of carbon emission) changes drastically depending on the fuel of the power plant.
About 4 out of 10 of power plants in the US run on coal, and when coal is burned to power electric cars, a little over 1.6 times the amount of CO2 a gas car would have emitted is released into the air. A little less than 3 out of ten power plants in the US run on natural gas, and when natural gas is burned to power electric cars, there is 80% as much CO2 released into the atmosphere. This means that when coal and natural gas are being used to power electric cars, there is 1.28x the amount of CO2 being released into the air, which happens in ⅔ of all the power plants in the US (about 1 in 10 power plants in the US run on clean, renewable energy) since the rest goes to nuclear and renewables (EPA). When renewables are added into the picture, the electric car wins out over gas cars, and on average emit 10% less CO2*.
*these statistics does not include electric cars powered from any other source than the electric grid, and does not take personally owned solar panels or turbines into account
energy efficiency- the ratio of energy used effectively to wasted energy
potential energy- energy yet to be used, stored in some form
drivetrain- the parts between the carriage of the car that transfer power from the engine to the wheels
mechanical energy- energy being transferred within a mechanical system
kinetic energy- energy being actively used, particularly for movement
Purpose of Lab: The purpose of this lab is to exhibit where and how the power grid makes electric cars less environmentally friendly than they appear.
Hypothesis: If electric cars release more CO2 into the air than gas cars, then they will require proportionately more megajoules to run than gas cars, because more fuels will have to be burned in the process of creating and transferring the electricity to power the electric cars than would be in a gas car’s engine.
Materials:
- ~30 lbs of wood
- 2 concrete blocks
- 1 gallon empty glass jug
- 2 quarts water
- Small Generator w/ windmill attachment
- Voltmeter
Procedures:
DO NOT TRY AT HOME
- Fill jug with 2 quarts water and put on cap, poke ½” hole in top
- IN A FIRE SAFE AREA Stand 2 blocks perpendicular to each other a little less than the diameter of the jug apart. Fill with wood and/or charcoal.
- Fit generator on stand so that turbine can spin over jug that will be placed on blocks
- Put jug over the wood and light carefully.
- Record energy being created with volt meter every 15 seconds for a minute and a half after it begins to boil
- Refuel wood and hookup wire to battery charger with battery and repeat process
Data Table:
The Electrical Output of the Generator Over Time
Time
|
Current Output
|
15 seconds
|
1.4 watts
|
30 seconds
|
1.9 watts
|
45 seconds
|
1.7 watts
|
60 seconds
|
1.6 watts
|
75 seconds
|
1.4 watts
|
90 seconds
|
1.2 watts
|
Conclusion Inquiry Questions:
Energy In The System
What do the different types of matter do? Why does it matter when and where the energy is created? Can the system be shorter and more efficient?
What causes the system to be environmentally unfriendly when powering electric cars? How can this be fixed?
___________________________________________________
How Are Antibodies Used for Blood Typing?-Lab Report
Introduction: As a part of our new unit on immunology, NEW school has designed a lab in which we can test and find our own blood types, so that we can further our knowledge on how antibodies and antigens work within our bodies. The reaction between the blood and the antigens will show us how foreign bodies are dealt with and will help us determine the specifics type of blood that is being reacted to.
Purpose: How are blood types and antigens correlated?
Hypothesis:
If my partner’s blood has antigen O presenting on the surface of her red blood cells, then none will precipitate or clump when placed in the serums, because the humoral system will not need to work towards homeostasis since O type blood is compatible with any type of blood.
Materials:
- Blood typing slide (4)
- Antisera A and B
- Anti-Rh factor
- Mixing sticks
- Blood samples
- Disposable gloves
Procedure: Using a toothpick, a different one for each well, place a drop of blood sample #1 in each well of a blood typing slide.
- Add a drop of anti-A to the well labeled A.
- Add a drop of anti-B serum to the well labeled B.
- Add a drop of anti-Rh serum to the well labeled Rh.
- Using a different toothpick for each well, gently stir the blood and antiserum drops for 30 seconds. Remember to discard each toothpick after a single use to avoid contamination to your samples.
- After 30 seconds of stirring carefully examine the liquid in the wells.
- If the liquid is clear or light pink with no particles or cloudiness formed, then no reaction has occurred and you should mark "No" in the appropriate box in the data table.
- If there are solid particles that have formed in mixing the sample or antiserum (they may be darker or lighter than the original liquid), then a reaction has occurred and you should mark "Yes" in the appropriate box. Also, if the liquid has very small particles formed, giving a cloudy appearance to the liquid, then a reaction has occurred and you should mark "Yes" in the appropriate box.
- It is important to look very closely at the wells and only do one well at a time. Be sure to stir at least 30 seconds with the plastic stick. The final product may be clear, white or dark pink depending on the combination of blood sample and antiserum, so look carefully to see if small or large particles have formed in the well.
Data Table:
Blood Reactions
Trail Number
|
Sample Number
|
Reaction with Anti-A (Y/N)
|
Reaction with Anti-B (Y/N)
|
Reaction with Anti-Rh (Y/N)
|
Determined Blood Type
|
1
|
1
|
none
|
none
|
none
|
O negative
|
Conclusion:
Blood typing and antigens are correlated to each other by reacting with specific antigens or not reacting to specific antigens. There was no reaction between the anti-A antigen, Anti-B antigen or anti-Rh antigen in the subject's blood. Since there were no precipitates formed, it can be concluded that the subject's blood was not rejected by any of the antigens. This means that the subject's blood type has to be O-, which is compatible with all other blood types and therefore with no opposing force from the B-cells in the blood the blood did not form a precipitate.
Immune System Intro
- What is the point of the immune system? To sustain homeostasis
- What is the difference between the first line of defense and second line of defense. The first line of defense is not active defense, but the second is.
- What is innate immunity mean? Immunity is the inability to be harmed.
- What is non-specific immunity mean? It means that of all the cells being killed to protect the body, some of them are good cells.
- What are three examples of first line of defense? Skin, hair, mucus, stomach acid
- What are the two examples of the second line of defense? Inflammation, white blood cells
- What is a pathogen? Pathogens are organisms like viruses that harm the body.
- What is a phagocyte? A type of cell that consumes bad bacteria or particles.
- What is major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II)? They mark which protein to kill.
- What is an antigen? A toxin that triggers an antibody response.
- What is a virus? - A complex collection of organic matter with the sole purpose of replicating
- What is the structure of a virus? (The anatomy of a virus) - A virus has a hard shell on the outside and DNA/RNA on the inside with enzymes.
- How do viruses work? - They infect healthy cells and hijack cells' replication process.
- How can a virus enter the body? - Viruses come from anywhere, and enter a cell pretending to be a protein
- What is bigger a virus or bacteria? - Virus
- How do viruses replicate? - Viruses hijack the cells' replication process.
- Compare Viral Tag to what you learned in the flipped classroom video. - In viral tag I learned that our immune system helps neutralize antibodies, and in the video I learned that a virus contains DNA or RNA.
Student Created Labs:
Question: What makes electric vehicles less energy efficient than gas vehicles?
Background Research:
- When electric cars are powered, they use electricity from the local grid
- The local grid is powered by the local energy plant, which can use coal, natural gas, solar, wind, hydropower, thermal, oil, biofuel, nuclear, wave, etc.
- A power plant works by burning fuel to heat up water so that it becomes steam and moves a turbine powering a generator, the electricity is gathered when the turbine is turned and rotates magnets around copper coils
- When power is gathered from renewable sources (besides biofuel), electricity is gathered straight away, like the turning of a wind turbine or the turning of a hydrowpower turbine at the bottom of a dam or electricity straight from solar, etc.
- When powering a car, the energy in a gas/diesel becomes kinetic energy in the engine, while the energy powering electric cars become kinetic in the power plant
- As of 2013, "about 65%" of energy is lost in the transfer from the power plant to your plug (EIA).
- At 13 gallons with 23.6 mpg When a power plant that uses burns petroleum is used to power an electric car
_____________________________________________________________________________
Vaccine Ingredients:
DTaP- most ingredients are toxic
- 5 benign
- 15 toxic
- Diptheria, Pertussis, Tetnis
MMR- Measles, Mumps, and Rubella
- 13 of the 13 ingredients are benign
HIB - the flu
- 4 ingredients benign
- lactose included
Hep B - 2 vaccines, first is 5 ingredients and second has 9
- 8 ingredients toxic
Hep A - 16 ingredients
- uses human abortion flesh for vaccine
- 3 non toxic
- 4 toxic
Varicella/Chickenpox/Varivax - 15 ingredients
- half toxic
HPV - STI vaccine
- prevents genital cancer
- most toxic
Who regulates the vaccines?
Who can have them?
Why are there so many ingredients?
_____________________________________________________________________________
Revamp of Science Assessment #7
The Varroa mite is the mite responsible for aiding the demise of the honeybee. The mite latches onto bees and hides in the hive by letting itself get encased in a brood cell with a bee larva. The larva grows up with a mite, and the eggs laid while in the pod hatch and infect the rest of the colony. Repeat cycle.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Our Common Lab Report Mistakes
After a lab write-up for our class DNA Lab, we discovered our common mistakes and how to handle them.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Fossil Fuels
Coal, oil, and natural gas are fossil fuels that were created from the remains of organic materials after being introduced to heat and pressure.
____________________________________________________________________________
Composition of Water Sources
The pH levels in numerous water sources give scientists an idea of how acidic or alkaline a source of water is and varies with the type of sources.
_____________________________________________________________________________
Pond:
macroscopic- don't need a microscope
photoautotrophs - create own food from light
heterotrophs - things that eat
Pond grows most bacteria because the water is stagnant and does not move
Bacteria can take over the pond, and when there is an imbalance there can be a surplus a specific material that can't be decomposed by the lack of a certain bacteria
Tap
Lead, Pesticides, Chlorine, Nitrates
Potable- drinkable fresh water
Corrosive- breaks down metal
Microbiological - microorganisms such as yeasts, fungi, bacteria, archaea, and protozoa
Chlorine reacts with other chemicals and has a low level of harm
Lead - never safe, most dangerous as a gas
PH of Ocean
8.0 to 8.4 pH of ocean
Low number is acidic, 0-7, high is alkaline, 7-14
Ocean pH was ~7 when tested
Bases- solutions that accept a H+
acids - solutions that donate a H+
Proton - positively charged particle in atom's nucleus
Extra releases of CO2 is absorbed by the ocean and turns into carbonic acid, and stops growth
___________________________________________________________________________
Condensation "Demo":
What happened:
- 6mL salt mixed with 1 L heated water
- Plastic wrap over bowl
- Ice put on top of bowl
Results:
The water was hot enough so that there was enough energy to change the liquid water into water vapor. The salt in the water has a higher vaporization temperature, so it remained in the water/salt solution. As this water vapor sat under the ice, it started to cool, until it reached the temperature in which water vapor turns back into liquid form again. This liquid water is seen under the ice, in a condensed patch.
____________________________________________________
The Water Cycle
Water stays in an
Evaporation, condensation, precipitation.
Vocab:
- clouds- condensed droplets of liquid water or ice particles around dust particles
- Percolation - is the process of a liquid slowly passing through a filter
- Sublimation (cold, dry, low pressure) - is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
- Transpiration - the process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere
- Desalination - the process of removing dissolved salts from water, thus producing fresh water from seawater or brackish water

Fig. 1 Openstax College. Biogeochemical Cycles: Figure 3 (2016) Image
Of all the types of water in the world, each one has a certain residence time. This time is how long water stays in a specific area without cycling and determines the content of water in a specific area.
 Fig. 1 Openstax College. Biogeochemical Cycles: Figure 1 (2016) Image |
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Figure 1. 2016. Openstacks CNX. Web. 8 March 2017
- Biogeochemical Cycle: Figure 3. 2016. Openstacks CNX. Web. 8 March 2017
_____________________________________________________________
Food Chain - Interactive
We took names of abiotic and biotic objects/animals/plants and assigned them to each student, these included the sun, grass, a snake, a rabbit, a hawk, etc. Each student then observed their fellow students, and considered how they interacted with each other, A student would hold a piece of yarn that was half red and half green. If the student represented anything that consumed another object/plant/animal, they would hold the red side of the yarn, and the object/plant/animal being consumed would hold the green side of the yarn. This created the food chain seen below.

____________________________________________________________________________
Ecology Vocabulary:
Ecology (noun) : study of how living things interact with each other and their enviornment
Ecosystem (noun) : all living and nonliving parts of an area and their interactions
Abiotic Factor (noun) : part of an ecosystem that is not alive
Biotic Factors (noun) : part of ecosystem that is alive
Adaptation (noun) : added characteristic that aids in the survival of an organism
Biome (noun) : large plant/animal communities
Detritivore (noun) : decomposers in an ecosystem
Community (noun) : a group of living organisms in a certain area
Consumers (noun) : organisms that survive by eating consumers
Carnivore (noun) : organisms that only eat consumers
Deforestation (noun) : the cutting down of trees and clearing of forest land
_____________________________________________________________________________
DNA
Enzyme Helicase splits DNA apart, the two strands' ending pairs are either 3 prime or 5 prime. the enzyme Polymerase lays down new nucleotides.
3 prime allows new nucleotides to be put down from the end of the strand going in. 5 prime is adding nucleotides towards the end of the DNA.
DNA is a long strand of 4 chemicals connected to a hydrogen bond "backbone" that makes up chromosomes inside of cells' nuclei. These extremely long strands of "code" dictates the functions of the living animal.
DNA is used for - Gene coding, DNA replication, and protein creation Nucleotides:
Guanine has covalent bonds with Cytosine
Adenine has covalent bonds with Thymine
The covalent bonds that hold together the nucleotides are relatively weak, for a reason.
We took names of abiotic and biotic objects/animals/plants and assigned them to each student, these included the sun, grass, a snake, a rabbit, a hawk, etc. Each student then observed their fellow students, and considered how they interacted with each other, A student would hold a piece of yarn that was half red and half green. If the student represented anything that consumed another object/plant/animal, they would hold the red side of the yarn, and the object/plant/animal being consumed would hold the green side of the yarn. This created the food chain seen below.
____________________________________________________________________________
Ecology Vocabulary:
Ecology (noun) : study of how living things interact with each other and their enviornment
Ecosystem (noun) : all living and nonliving parts of an area and their interactions
Abiotic Factor (noun) : part of an ecosystem that is not alive
Biotic Factors (noun) : part of ecosystem that is alive
Adaptation (noun) : added characteristic that aids in the survival of an organism
Biome (noun) : large plant/animal communities
Detritivore (noun) : decomposers in an ecosystem
Community (noun) : a group of living organisms in a certain area
Consumers (noun) : organisms that survive by eating consumers
Carnivore (noun) : organisms that only eat consumers
Deforestation (noun) : the cutting down of trees and clearing of forest land
_____________________________________________________________________________
DNA
Enzyme Helicase splits DNA apart, the two strands' ending pairs are either 3 prime or 5 prime. the enzyme Polymerase lays down new nucleotides.
3 prime allows new nucleotides to be put down from the end of the strand going in. 5 prime is adding nucleotides towards the end of the DNA.
DNA is a long strand of 4 chemicals connected to a hydrogen bond "backbone" that makes up chromosomes inside of cells' nuclei. These extremely long strands of "code" dictates the functions of the living animal.
DNA is used for - Gene coding, DNA replication, and protein creation Nucleotides:
Guanine has covalent bonds with Cytosine
Adenine has covalent bonds with Thymine
The covalent bonds that hold together the nucleotides are relatively weak, for a reason.
These bonds are hydrogen bonds because hydrogen bonds are the weakest of all covalent bonds, making the splitting of the nucleotides easier.
This splitting of these nucleotides is a crucial step in the reproduction of the DNA, as the DNA is split in half between the nucleotides into 2 RNA strands in transcription.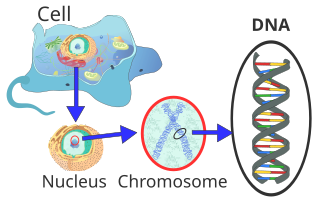



____________________________________________________________
The Science of Addiction
Addiction is a very serious matter, especially if it's with a chemical agent. This is how it works.
Addiction starts in the brain, even though the brain stem and cerebral cortex are involved, the main component in addiction is the limbic system. This system is responsible for our moods and sense of pleasure after an action that is perceived as good for our body, which explains why it is the biggest component in addiction.
___________________________________________________
Left Frontal Lobe Stroke
Below is an example of a possible explanation of the condition as well as treatment options to a patient who underwent a stroke of the left frontal lobe from a doctor.
_________________________________________________________________________________The Science of Addiction
Addiction is a very serious matter, especially if it's with a chemical agent. This is how it works.
Addiction starts in the brain, even though the brain stem and cerebral cortex are involved, the main component in addiction is the limbic system. This system is responsible for our moods and sense of pleasure after an action that is perceived as good for our body, which explains why it is the biggest component in addiction.
___________________________________________________
Left Frontal Lobe Stroke
Below is an example of a possible explanation of the condition as well as treatment options to a patient who underwent a stroke of the left frontal lobe from a doctor.
Two weeks when you experienced an ischemic stroke, there was a blood clot that blocked a blood vessel in the left frontal lobe of your brain. That is why you experienced a complete loss of function to your right leg and partial loss of function to your right arm. Your speech was also greatly impaired because of this and is an explanation for your lacking of reasoning prior to the event.
When you were talking to your relative on the phone at the time of the incident and she noticed that after your first complaints of numbness in your right leg, you started mumbling unreasonable phrases which regressed to incoherent fragments of phrases. When your relative noticed this she immediately rushed to your house within 15 minutes which is why you have no severe cases of paralysis, had she been an hour late you most likely would not be able to walk.
Your initial medicine given was the tPA clot buster, but now I am going to prescribe you some blood thinners to prevent the clots as well as speech rehabilitation and physical therapy to get your walking back (since you complain of still some numbness in your right leg and complicated balance) and to perfect your speech again. It is rare that a patient who suffers a frontal lobe stroke does not have memory problems so if that seems to be a problem call me right away. We’re also going to give you statin to slow your liver’s production of cholesterol because we think that was the cause of the blockage in your blood vessel. Just as a closing note it is a good idea be aware of how cautious you seem to be now, especially while driving, because frontal lobe stroke patients tend to exert more cautious and careful behavior.
"What Is a Big Stroke in the Cerebral Cortex?" Verywell. N.p., n.d. Web. 02 Dec. 2016.
“Changes Caused by Stroke”. Columbia, SC: South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control, 2005. Web. 07 Dec. 2016
"Brain Lobes and Effects of Strokes." UW Health, University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics 2016. Web. 7 Dec. 2016.
"Know Stroke. Know the Signs. Act in Time." National Institutes of Health. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Jan 2008. Web. 08 Dec. 2016.
Mapping Of the Brain
In science class we cut open a cauliflower that represented a human brain.
Our group decided to cut the brain in half, by keeping the anterior and posterior on each piece and separating the left and right sides of the brain. Then we procedded to label it.
The Pieces:
The sections of the brain are pointed out with color coordinated toothpicks.
The Lobes:
(Yes it it is hard to see the division between the lobes, this was due to a weekend in the refrigerator in which one or two toothpics fell out from overcrowding, so the next picture is our target we aimed for)
The bluegreen toothpick on the far left (the anterior) broke off and was misplaced, its intended placement was on the far posterior, where you can see the broken toothpick that represents the occipital lobe
The orange toothpick was taken out and put too close to the anterior, and should be moved ~3 inches to the right, it represents the temporal lobe
The blue toothpick is the cerebral cortex
The purple toothpick represents the parietal (highest purple toothpick)
The violet toothpick represents the cerebellum (lowest purple toothpick)
The dark green toothpick represents the brain stem
The red toothpick represents the frontal lobe

_________________________________________________________________________________
Iron Chef Pesticides
Team One:
the pesticides effect plants and fungi, fed yeast, added pesticides to to three beakers, added pesticides to basil plants, pesticides effect the foods we eat, correct hypothesis, well put together, look official, overall great presentation, would change control group
Team Two:
If organic and conventional sample of ground chuck, and apples are exposed to pesticides, the organic's food's cellular structure will be more damaged by the pesticides than non organic foods, because non organic food has been altered to resist pesticides, make agar, organic was more affected, little differences, more diversity in organic, more controlled setting, ants, more time, well done, possibly explain more of how the experiment went, explain hypothesis
Iron Chef Sugars
Team One:
If bacteria is exposed to 3 different types of sugars: light fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, and honey on 15 individual Petri dishes for a period of 1 week, then the bacteria with the light fructose corn syrup will grow a substantial amount of bacteria compared to the plates with the cane sugar and the honey because the light fructose corn syrup is full of the added chemicals from the production of corn and when the unhealthy sugars are added to the corn syrup, it will cause a greater reaction because it stimulated the bacteria, make agar,put in an incubator, swabbed bacteria, watched bacteria growth for 2 weeks,found results, honey had the most growth, then cane, then corn, the processing in food can possibly cause cancer, well put together, a little lengthy
Team Two:
If six students, three boys, three girls, get their glucose levels tested for one week on their regular diet then three more weeks while substituting in honey, sugar, and corn syrup into their diet then the corn syrup will have the greatest increase in glucose levels, because corn syrup has a higher glycemic index in it which increases the blood sugar, and the higher the glycemic index the higher the glucose levels are, took blood sugar levels,document, found results, honey caused the highest glucose level, tested blood sugar level before and after given the ingredient, reliability, well put together, great experiment
Iron Chef Drinks
Team One:
If a person drinks 20 ml of the bolthouse green smoothie, then they will have more natural bacterial growth in their mouth compared to the same person the same person when they drink 20 ml of the coca cola because the soda has artificial sugars and the bolthouse green smoothie drink contains natural sugars, swabbed teeth with cotton swabs, most plaque on soda the coffee, then the smoothie, then Listerine, then water, accurate scale, an incubator malfunctions, well put together, very interesting experiment
Team Two:
If yeast is given different liquids with varying amount of natural and artificial sugars in bottles with balloons on top, then the bottle with the most natural sugar will inflate the balloon the most because the yeast will thrive with the natural sugars causing the yeast to release more carbon dioxide, used yeast, observed the difference over a period of time, more controlled setting, get more materials, very interesting
Iron Chef Lab Report (If this section is hard to read I encourage you to click this link)
Dissolution of Organic and Non Organic Strawberries
Introduction: This lab was designed to find results regarding dietary preference* in terms of organic and non-organic (conventional) foods. The results were determined on how well either foods dissolved in two different types of enzymes and water. The dissolution of the strawberries were determined by the displacement of the water, which when assuming evaporation is constant, indicates the increase of density and therefore the amount dissolved into the water and/or enzyme. This ties into bodily reactions because any portion of food that is not broken down by the body is considered indigestible, and may harm the body when the liver cannot detoxify all of these indigestible food particles, which is why this lab focuses on the breakdown of the food.
Purpose: To find out if either organic** or conventional foods are more digestible than one another.
Hypothesis: If 8, 18 gram strawberries were each individually placed in all 8 jars of 300mL water and either Pectinase, Amylase, Pectinase and Amylase, or plain water until they dissolved, then the organic strawberries will dissolve the best, because the preservatives and chemicals in the conventional strawberries will not be compatible with the enzymes, and therefore unable to undergo chemical digestion.
Materials:
Procedure:
1.Label all the beakers with their assigned name (org. Amylase, organic pectinase, conv. Pectinase, conv. Water, conv. Pectinase and amylase, organic water, organic pectinase and amylase, conv. amylase)
2. Measure pectinase and amylase in scale as 24 g
3. Measure distilled water in all beakers as 300 ml
4. Measure out 8 grams of pectinase, 8 grams of amylase, two beakers with 4 grams amylase and grams of pectinase each, then 2 beakers left empty
5. Add the 300 mL of distilled water to each beaker
6. Take off the stem of the strawberries
7. Measure the strawberries to 18g for all of the strawberries to be the same
8. If the strawberries are not 18g exactly, cut off the extra grams to eliminate the excess grams
9. Take both 4 organic and 4 conventional strawberries and put them in their corresponding container
10.Put beakers filled with pectinase and amylase in the store room, hidden from the light
11.Measure the displacement
12.Record the data that you see as the effects take place
Data Table:
Identify the Independent and Dependent Variable:
The independent variable was the amount and kind of breakdown substance used as well as the amount of strawberries.
The dependent variable was the amount the displacement of the object.
Graph:
Conclusion:
Claim – The organic foods would have a larger displacement because they would dissolve better in the enzymes since there is no chemicals that wouldn’t be compatible with the enzymes.
Evidence – The displacements of the strawberries are conventional amylase with 11mL, organic amylase with 1.8 mL, conventional pectinase and amylase with 6.4 mL, organic pectinase and amylase with 11 mL, conventional pectinase with 20.2 mL, and organic pectinase with 15.8 mL.
Reasoning – According to this data, there is no difference between organic and conventional foods, because there are no definitive trends within the data to claim otherwise. Both averages for displacement fell well within the margin of error, and therefore can be marked as non differential.
|
* It is not recommended to only take into account only this study’s data and conclusion
** Industrial organic
The Process of Cellular Respiration
The point of cellular respiration is to turn sugar and oxygen into ATP (the source of energy for cells). The balanced chemical equation looks like this:

The first step of this process is glycolosis, which is the initial breakdown of sugar molecules (represented as the cake mix). The 6 sugar carbons are broken in half into two 3 carbon molecules called pyruvate. This occurs in the cytoplasm (the eggs and oil) of the cell and requires 2 ATP to commence, and makes 4 ATP.
The next step occurs in the cell's mitochondrias' inner membrane and is called the Krebs Cycle. This aerobic cycle involves turning the product from glycolosis (pyruvate) into another product, this time ATP and Hydrogen+ while the byproduct of this cycle for is CO2. When done anaerobically, the product for animals is lactic acid and alcohol for plants. The NAD+ (the ladel) coenzymes transport the H+ product (the batter) from the cycle directly to the electron transport chain after the cycle spits each H+ out.
The electron transport chain also occurs in the mitochondrial membrane and has an output of about 28-34 ATP. It involves a proton gradient (brownie pan with brownie batter), which takes multiple H+ at time and throws them into the enzyme ATP Synthase with ADP to make the ATP, with a byproduct of H20.

_________________________________________________________________________________
Lab: Yeast, Sugar, Water, Acid, Base, and Heat
"Purpose: see how sugar is affected by the differences of temperature"
add 50mL of sugar added to all
21 g of yeast added to all
nothing added
25 mL of lemonade added
25 mL of baking soda
200 mL cold water
200 mL hot water
200 mL room temp
_________________________________________________________________________________
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM:
The first step of human digestion is in the mouth by mechanical and chemical processes. The food is torn and mashed by the incisors and molars, a mechanical process. Then the chunks and pieces begin their chemical breakdown by the amylase enzymes in the saliva that take particles and react with them.
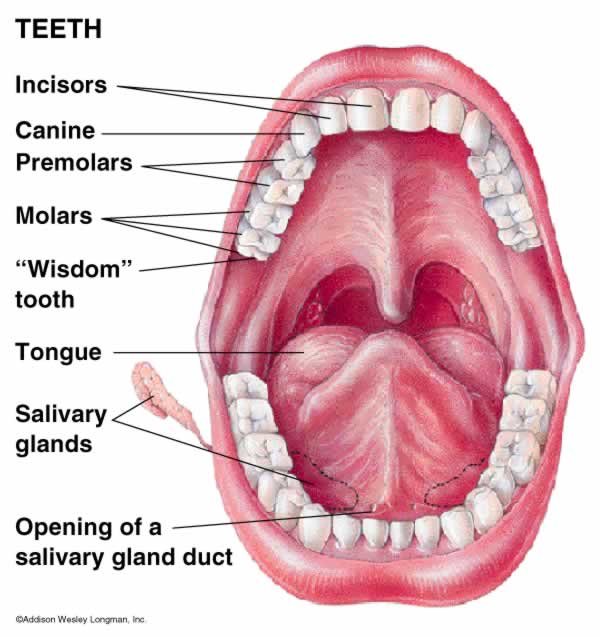
Next the food travels down the esophagus into the stomach, where is is mixed around and introduced to hydrochloric acid and the enzyme pepsin, which further the breakdown by chemical means. The flexibility of the stomach is crucial for mixing the substances together, which by the way, is a mechanical function.

From the stomach the food travel out the pyloric sphincter to the small intestine, where the acid is countered by base furthering nutrients. The small intestine's job is to extracts the nutrients from the food, and it does this along a tract about nine meters long! Most of these nutrients go straight to the liver.
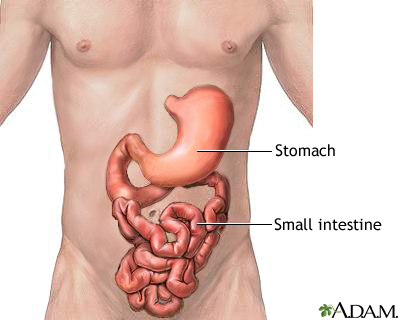
From the small intestine food travels to the large intestine, which dries out the food by sending in nutrients that dissolve in the water, then extracting the solution, This is because there needs to be a balance of dry and moist fecal matter for easiest extraction. After passing through this tract, food is sent to the rectum.
The rectum stores the fecal matter that had been dried out by the large intestine, and helps push it out of the anus when the body is ready for it to be defecated.
Comments
Post a Comment